if와 switch 구문으로 조건문을 만들 수 있고, for-in, while, repeat-while로 반복문을 만들 수 있다. 반복문 주위 ()는 선택적이다. 반복문 몸통의 앞뒤 {}는 필수 요소이다.
let individualScores = [75, 43, 103, 87, 12]
var teamScore = 0
for score in individualScores {
if score > 50 {
teamScore += 3
} else {
teamScore += 1
}
}
print(teamScore)
// Prints "11"if 조건문에서, 조건문은 반드시 Boolean expression이어야 한다. if score { ... }와 같이 표현하면 score는 암시적으로 0과 비교되지 않고 오류가 발생한다.
if와 let을 함께 사용하여 nil이 될 수 있는 값을 선언할 수 있다. 이러한 값은 optional하게 표현된다. optional 값은 해당 변수 타입 값 또는 nil을 값으로 갖는다. 타입 뒤에 ?를 붙여 optional type을 만들 수 있다.
var optionalString: String? = "Hello"
print(optionalString == nil)
// Prints "false"
var optionalName: String? = "John Appleseed"
var greeting = "Hello!"
// optionalName이 nil인 경우 { ... }는 실행되지 않는다.
if let name = optionalName {
greeting = "Hello, \(name)"
}optionalName이 nil이면 let name = optionalName은 false가 되어 if 문을 패스한다.
optional 값을 제어하는 또다른 방법은 ??와 함께 디폴트 값을 정해주는 것이다.
let nickname: String? = nil
let fullName: String = "John Appleseed"
let informalGreeting = "Hi \(nickname ?? fullName)"if 문과 달리 switch 문은 어떤 종류의 값이 들어오더라도 대응할 수 있다. 다음 switch 문에서 let이 어떻게 사용되는지 확인해보자.
let vegetable = "red pepper"
switch vegetable {
case "celery":
print("Add some raisins and make ants on a log.")
case "cucumber", "watercress":
print("That would make a good tea sandwich.")
case let x where x.hasSuffix("pepper"):
print("Is it a spicy \(x)?")
default:
print("Everything tastes good in soup.")
}
// Prints "Is it a spicy red pepper?""pepper"를 접미사로 갖는 모든 케이스가 case let x where x.hasSuffix("pepper"):에 해당한다.
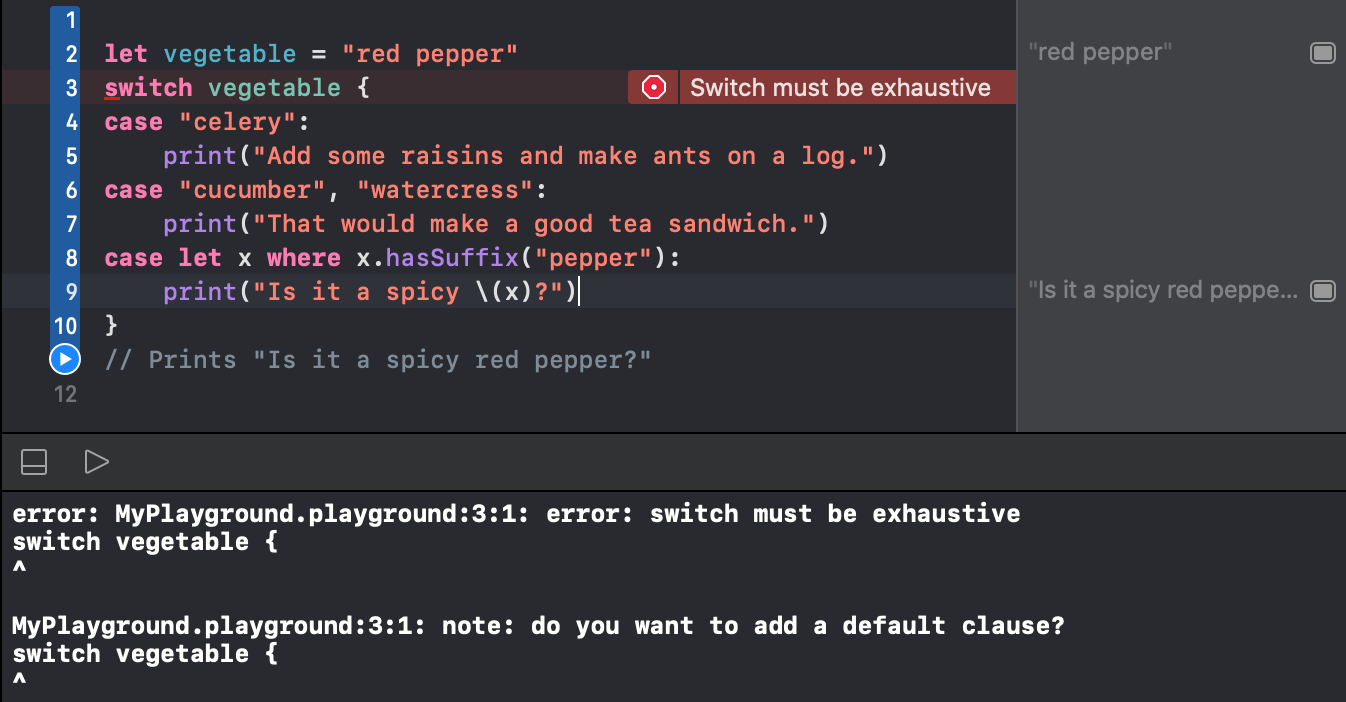
default 케이스를 지운다면 다음과 같은 에러가 발생한다. default에서 아무 구문도 실행하고 싶지 않다면 break를 통해 탈출하면된다.
for-in 구문을 사용하여 딕셔너리의 키와 값을 iterate 할 수 있다. 딕셔너리는 순서가 정해져 있지 않은 collection이므로, 키와 값의 순서가 임의적으로 선택된다.
let interestingNumbers = [
"Prime": [2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13],
"Fibonacci": [1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8],
"Square": [1, 4, 9, 16, 25],
]
var largest = 0
for (kind, numbers) in interestingNumbers {
for number in numbers {
if number > largest {
largest = number
}
}
}
print(largest)
// Prints "25"while 문을 사용하여 컨디션이 충족될 때까지 해당 블록을 실행할 수 있다. repeat-while문은 다른 언어의 do-while과 같은 효과를 갖는다.
var n = 2
while n < 2 {
n *= 2
}
print(n) // prints "2"
n = 2
repeat {
n *= 2
} while n < 2
print(n) // prints "4"인덱스 range를 만들기 위해 ..< 문법을 사용할 수 있다.
var total = 0
for i in 0..<4 {
total += i
}
print(total) // prints "6"
total = 0
for i in 0...4 {
total += i
}
print(total) // prints "10"0..<4는 0, 1, 2, 3을 포함하는 범위이지만, 0...4는 0~4를 포함한다.
'Swift' 카테고리의 다른 글
| mac OS #Framework 생성, Cannot find #FUNCTION in scope error, Swift #접근제어자 와 @testable (0) | 2021.01.21 |
|---|---|
| #Postman 이용하여 #대부분의 데이터를 받아오는 방법! (0) | 2021.01.20 |
| Objects and Classes - A Swift Tour 3일차 (0) | 2020.12.21 |
| Functions and Closures - A Swift Tour 2일차 (0) | 2020.12.19 |
| Simple Values - A Swift Tour 1일차 (0) | 2020.12.19 |

