반응형
classroom.udacity.com/courses/cs373/lessons/48723604/concepts/486836600923
Udacity
classroom.udacity.com
UPDATE
다음은 칼만 필터 업데이트에 사용되는 기호와 의미입니다. 근데 외우지말래요...
- X = estimate
- F = state Function matrix
- u = motion vector
- P = uncertainity covariance
- Z = measurement
- H = measurement function
- R = measurement noise
- y = error
- k = Kalman gain
- I = identify matrix
Prediction


measurement update



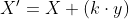

아무튼 이렇다고 합니다.
Multi-Dimension Kalman Filter Update in Python
템플릿 코드는 다음과 같으며, 프로그램의 목표는 00하는 것입니다. matrix는 행렬, transpose는 전치행렬을 의미합니다. 위 식과 아래 matrix 라이브러리를 이용하여 칼만 필터를 해결해봅시다. kalman_filter(x, P) 함수의 비어있는 for 문을 채워보세요!!
# Write a function 'kalman_filter' that implements a multi-
# dimensional Kalman Filter for the example given
from math import *
class matrix:
# implements basic operations of a matrix class
def __init__(self, value):
self.value = value
self.dimx = len(value)
self.dimy = len(value[0])
if value == [[]]:
self.dimx = 0
def zero(self, dimx, dimy):
# check if valid dimensions
if dimx < 1 or dimy < 1:
raise ValueError, "Invalid size of matrix"
else:
self.dimx = dimx
self.dimy = dimy
self.value = [[0 for row in range(dimy)] for col in range(dimx)]
def identity(self, dim):
# check if valid dimension
if dim < 1:
raise ValueError, "Invalid size of matrix"
else:
self.dimx = dim
self.dimy = dim
self.value = [[0 for row in range(dim)] for col in range(dim)]
for i in range(dim):
self.value[i][i] = 1
def show(self):
for i in range(self.dimx):
print(self.value[i])
print(' ')
def __add__(self, other):
# check if correct dimensions
if self.dimx != other.dimx or self.dimy != other.dimy:
raise ValueError, "Matrices must be of equal dimensions to add"
else:
# add if correct dimensions
res = matrix([[]])
res.zero(self.dimx, self.dimy)
for i in range(self.dimx):
for j in range(self.dimy):
res.value[i][j] = self.value[i][j] + other.value[i][j]
return res
def __sub__(self, other):
# check if correct dimensions
if self.dimx != other.dimx or self.dimy != other.dimy:
raise ValueError, "Matrices must be of equal dimensions to subtract"
else:
# subtract if correct dimensions
res = matrix([[]])
res.zero(self.dimx, self.dimy)
for i in range(self.dimx):
for j in range(self.dimy):
res.value[i][j] = self.value[i][j] - other.value[i][j]
return res
def __mul__(self, other):
# check if correct dimensions
if self.dimy != other.dimx:
raise ValueError, "Matrices must be m*n and n*p to multiply"
else:
# multiply if correct dimensions
res = matrix([[]])
res.zero(self.dimx, other.dimy)
for i in range(self.dimx):
for j in range(other.dimy):
for k in range(self.dimy):
res.value[i][j] += self.value[i][k] * other.value[k][j]
return res
def transpose(self):
# compute transpose
res = matrix([[]])
res.zero(self.dimy, self.dimx)
for i in range(self.dimx):
for j in range(self.dimy):
res.value[j][i] = self.value[i][j]
return res
# Thanks to Ernesto P. Adorio for use of Cholesky and CholeskyInverse functions
def Cholesky(self, ztol=1.0e-5):
# Computes the upper triangular Cholesky factorization of
# a positive definite matrix.
res = matrix([[]])
res.zero(self.dimx, self.dimx)
for i in range(self.dimx):
S = sum([(res.value[k][i])**2 for k in range(i)])
d = self.value[i][i] - S
if abs(d) < ztol:
res.value[i][i] = 0.0
else:
if d < 0.0:
raise ValueError, "Matrix not positive-definite"
res.value[i][i] = sqrt(d)
for j in range(i+1, self.dimx):
S = sum([res.value[k][i] * res.value[k][j] for k in range(self.dimx)])
if abs(S) < ztol:
S = 0.0
try:
res.value[i][j] = (self.value[i][j] - S)/res.value[i][i]
except:
raise ValueError, "Zero diagonal"
return res
def CholeskyInverse(self):
# Computes inverse of matrix given its Cholesky upper Triangular
# decomposition of matrix.
res = matrix([[]])
res.zero(self.dimx, self.dimx)
# Backward step for inverse.
for j in reversed(range(self.dimx)):
tjj = self.value[j][j]
S = sum([self.value[j][k]*res.value[j][k] for k in range(j+1, self.dimx)])
res.value[j][j] = 1.0/tjj**2 - S/tjj
for i in reversed(range(j)):
res.value[j][i] = res.value[i][j] = -sum([self.value[i][k]*res.value[k][j] for k in range(i+1, self.dimx)])/self.value[i][i]
return res
def inverse(self):
aux = self.Cholesky()
res = aux.CholeskyInverse()
return res
def __repr__(self):
return repr(self.value)
########################################
# Implement the filter function below
def kalman_filter(x, P):
for n in range(len(measurements)):
# measurement update
# prediction
return x,P
############################################
### use the code below to test your filter!
############################################
measurements = [1, 2, 3]
x = matrix([[0.], [0.]]) # initial state (location and velocity)
P = matrix([[1000., 0.], [0., 1000.]]) # initial uncertainty
u = matrix([[0.], [0.]]) # external motion
F = matrix([[1., 1.], [0, 1.]]) # next state function
H = matrix([[1., 0.]]) # measurement function
R = matrix([[1.]]) # measurement uncertainty
I = matrix([[1., 0.], [0., 1.]]) # identity matrix
print(kalman_filter(x, P))
# output should be:
# x: [[3.9996664447958645], [0.9999998335552873]]
# P: [[2.3318904241194827, 0.9991676099921091], [0.9991676099921067, 0.49950058263974184]]
수식의 구현일 뿐이라 어렵지 않습니다...만, 측정값 Z를 표현하는 데에 있어서 오답이 한두 번 정도 있었습니다. measurements는 정수 배열이지만 y를 계산하기 위해선 matrix 형태가 되어야 하죠. measurements 값을 쉽게 받아오기 위해 for 문의 형식도 약간 변경하였습니다.
def kalman_filter(x, P):
for Z in measurements:
# measurement update
S = H * P * H.transpose() + R
k = P * H.transpose() * S.inverse()
y = matrix([[Z]]) - (H * x)
x = x + k * y
P = (I - k * H) * P
# prediction
x = F * x + u
P = F * P * F.transpose()
return x,P이러한 과정을 거쳐 우리의 자율주행 자동차는 다른 차를 탐지할 수 있습니다. 정말 이해한 걸까?? 하는 생각은 들지만요....
반응형
'Robotics' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 42일차 - 4D Kalman Filter (0) | 2020.08.15 |
|---|---|
| 41일차 - 매니퓰레이션 소개 및 URDF 작성법 (0) | 2020.08.12 |
| 39일차 - 2차원 Kalman Filter, Position과 Velocity의 상관관계 (0) | 2020.08.12 |
| 38일차 - 칼만 필터 이동과 예측 알고리즘, 파이썬 코드 (0) | 2020.08.11 |
| 37일차 - 2D Localization (0) | 2020.08.06 |



